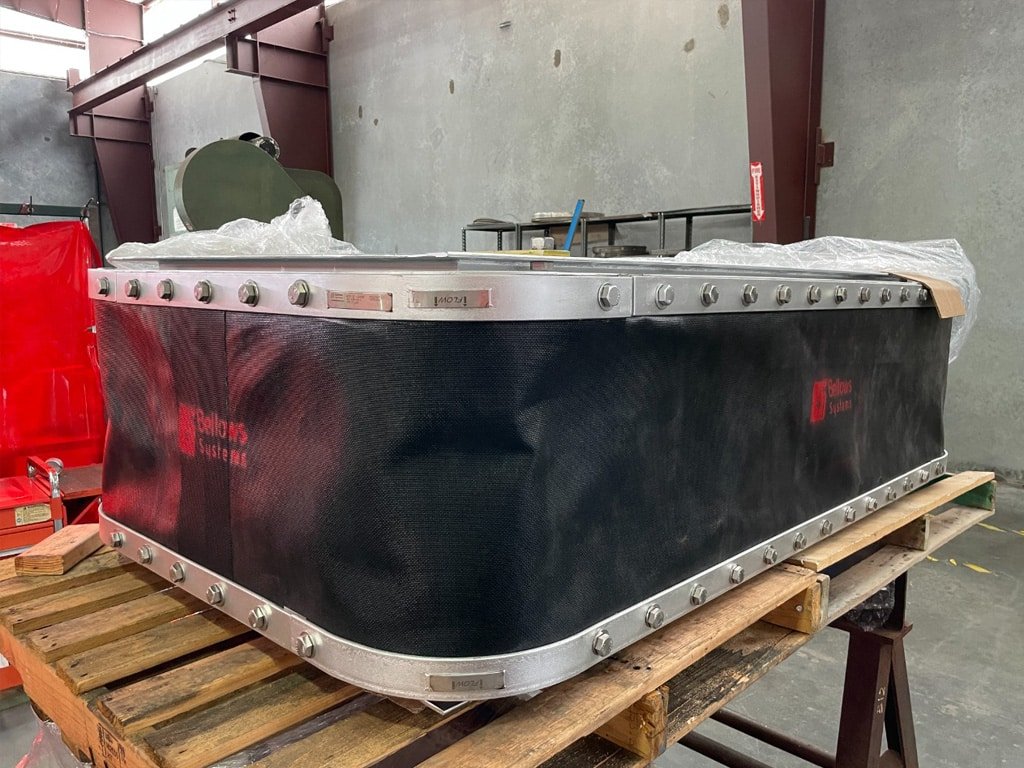
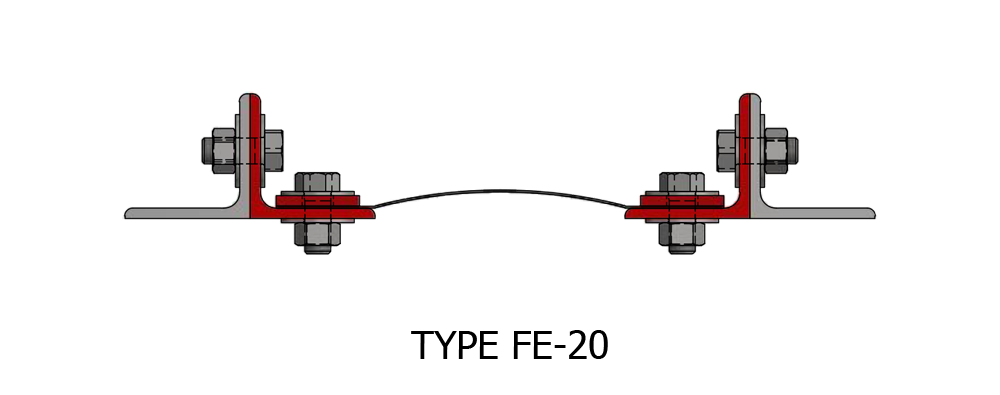
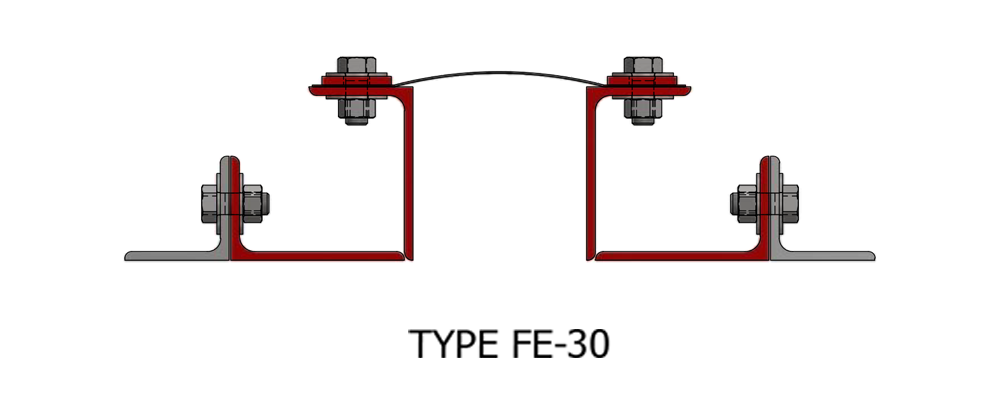
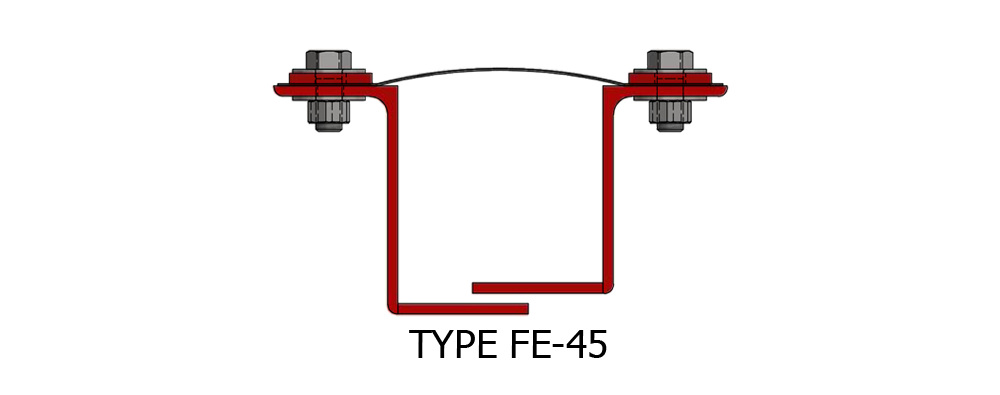
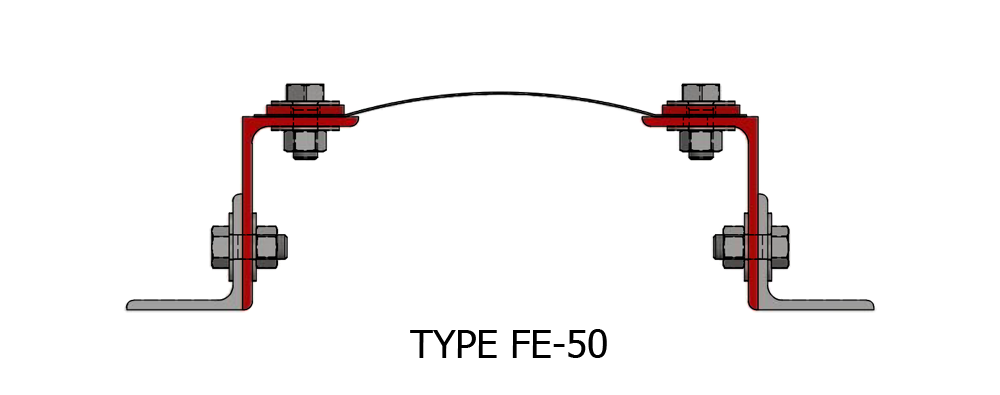
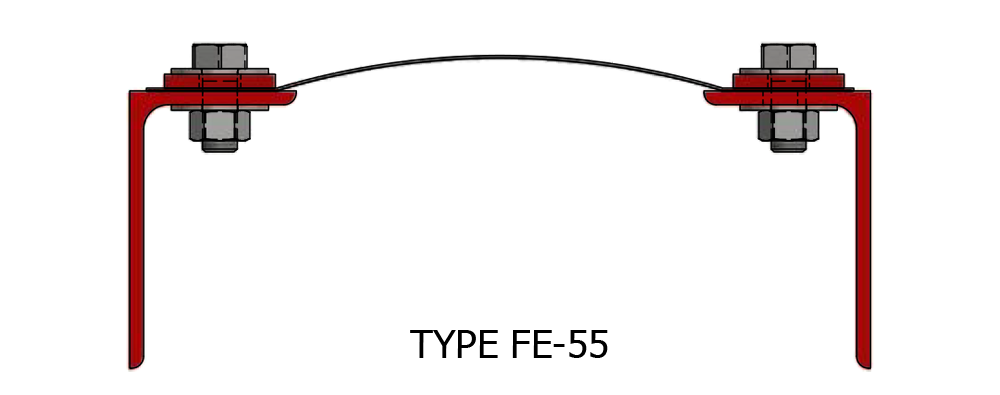
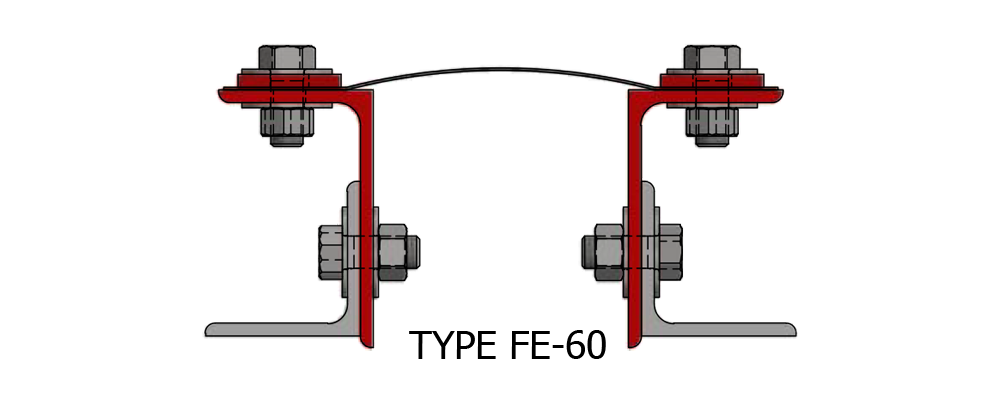
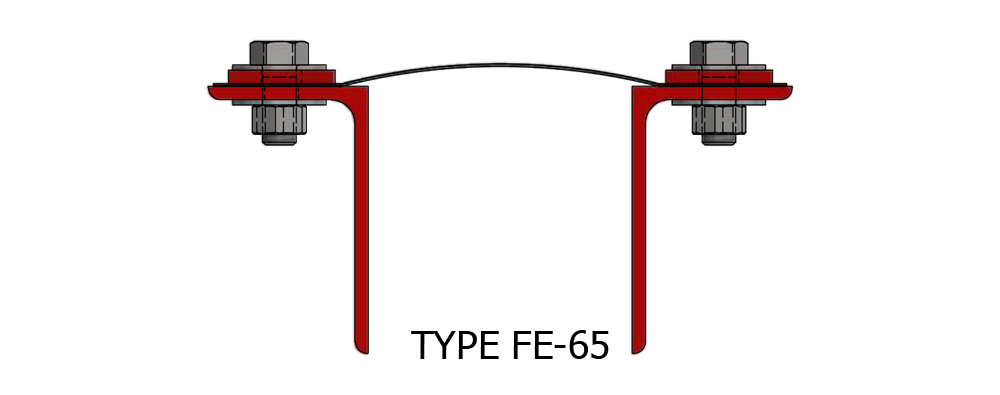
Composite Fabric Expansion Joint for low pressure ducting applications.
Fabric Expansion Joints utilize a composite fabric material as the flexible element of the expansion joint. They are typically used in low pressure ducting applications to compensate for misalignment, vibration and thermal growth. Fabric expansion joints can be designed with composite fabric with integral insulating layers or separate insulation pillows to handle temperatures in excess of 1000˚F.
Fabric Expansion joints can used to compensate thermal growth in ducting and misalignment without the spring loads typically associated with metal expansion joints. Fabric expansion joints can also absorb large lateral movements or misalignments. Additional components, like flow liners, insulation blankets and accumulation barriers can be added to the fabric expansion joint depending on the application and service.
BSI Therma-Joint Flexible Expansion Joints – for high temperature applications like Turbine Exhaust.
Standard Construction: Layered high Temperature fiber glass cloth, stainless foil and stainless steel mesh stitched together to form a unitized insulating expansion joint. The standard design is able to endure temperature of 1200˚F and to eliminate excessive vibration associated with the transfer of hot gases through the ducting systems of gas turbines and furnaces. Therma-Joints can be designed to withstand temperatures up to 2500˚F.
Fabric Expansion Joint Types
Assembly: Belt Type or Flange Type
Shapes: Circular or Rectangular
Optional Features:
- Liners (Drop in or Integral)
- Insulation sleeves/ Accumulation barrier
- Control rods
Standard Performance Data:
Temperature Range: -20˚F to 1200˚F
Pressure Range: -60in to 60in of water (H2O) column.
Movement Range:
| Belt Width | Axial Comp | Axial Ext | Lat Mov |
| 12″ | 4.5″ | 2.5″ | 2.5″ |
| 18″ | 6″ | 3″ | 4″ |
| 24″ | 6″ | 4″ | 5″ |
To learn more about our Fabric Expansion Joint or other products, call us at (800) 233-0623 or email us at info@bellows-systems.com.
Frequently Asked Questions
Fabric expansion joints offer several benefits when used in ducting systems. Here are some of the key benefits:
Absorb thermal and mechanical movements: Fabric expansion joints can absorb thermal and mechanical movements in ducting systems, which can occur due to changes in temperature, pressure, or vibration. This helps to prevent damage to the ducting system and other components, such as fans, dampers, and filters.
Reduce stress on ducting and equipment: Fabric expansion joints can reduce stress on the ducting system and equipment by absorbing thermal and mechanical movements. This can help to extend the lifespan of the ducting system and equipment, reduce maintenance costs, and improve reliability.
Provide vibration isolation: Fabric expansion joints can provide vibration isolation by absorbing vibration and shock in the ducting system. This helps to protect equipment from damage and reduce noise levels.
Offer cost-effective solutions: Fabric expansion joints are often more cost-effective than other types of expansion joints, such as metal expansion joints. They require less maintenance and can be designed to fit a wide range of applications and operating conditions.
Allow for flexibility in ducting design: Fabric expansion joints can be designed to fit a wide range of ducting configurations and movements, including angular, lateral, and axial movements. This allows for greater flexibility in ducting design and can help to reduce the number of ducting components required.
Provide chemical resistance: Fabric expansion joints can be designed to provide chemical resistance, making them suitable for use in corrosive environments. This can help to reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the ducting system and equipment.
Overall, fabric expansion joints offer several benefits when used in ducting systems, including absorbing thermal and mechanical movements, reducing stress on ducting and equipment, providing vibration isolation, offering cost-effective solutions, allowing for flexibility in ducting design, and providing chemical resistance.
Fabric expansion joints are commonly used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
Power generation: Fabric expansion joints are used in power generation applications, such as gas turbine exhaust systems, HRSG ducting systems, and boiler air and flue gas systems.
Cement plants: Fabric expansion joints are used in cement plants, such as kiln inlet and outlet seals, and raw mill inlet and outlet ducts.
Steel mills: Fabric expansion joints are used in steel mills, such as blast furnace stoves, coke oven doors, and hot air ducts.
Chemical processing: Fabric expansion joints are used in chemical processing applications, such as reactor exhaust systems, acid and alkali scrubbers, and flue gas desulfurization systems.
Petrochemical processing: Fabric expansion joints are used in petrochemical processing applications, such as refinery flue gas systems, catalytic crackers, and thermal oxidizers.
Marine: Fabric expansion joints are used in marine applications, such as exhaust systems for ships and boats.
HVAC: Fabric expansion joints are used in HVAC applications, such as air handling units, and ducting systems.
Food processing: Fabric expansion joints are used in food processing applications, such as baking ovens and drying systems.
Pulp and paper: Fabric expansion joints are used in pulp and paper applications, such as lime kilns and recovery boiler ducting systems.
Overall, fabric expansion joints are used in a wide range of industries and applications where there is a need to absorb thermal and mechanical movements, reduce stress on ducting and equipment, provide vibration isolation, offer cost-effective solutions, allow for flexibility in ducting design, and provide chemical resistance.
The temperature and pressure range of fabric expansion joints can vary depending on the materials used in their construction and the specific design of the joint.
Typically, fabric expansion joints can operate at temperatures ranging from -50°C to over 1000°C (-58°F to over 1832°F), and can handle pressures ranging from vacuum up to few psi. The exact temperature and pressure range of a specific fabric expansion joint will depend on factors such as the materials used in its construction, the design of the joint, and the specific application in which it will be used.
If you are interested in learning more about the temperature and pressure range of Bellows Systems’ fabric expansion joints, please contact our technical support team for more information.